
[Option, choice] BS
Here you can choose whether a criterion is set to
the comfort of the climate inside in summer conditions. The following criteria
can be applied:
§ ULH [° C and hours] stands for unmet load hours. If the inside air temperature, which is calculated every hour, exceeds the specified temperature, this will be added to the number of temperature overshoots. A maximum of two criteria can be specified. These general criteria are translated into the allowed temperature overshoots for design activities in an office environment by the Dutch Government Buildings Agency. In this translation the outside climate anno 1964 is used as a reference: it is not allowed to exceed 25 °C for more than 100 hours per year and to exceed 28 °C more than 20 hours a year. For more information, see http://www.comnet.org/mgp/content/23-unmet-load-hours.
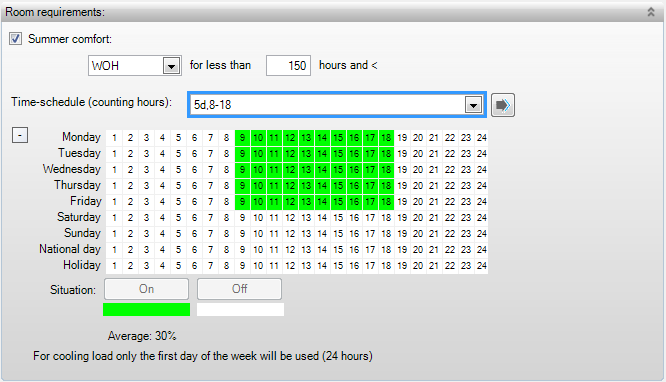
§ WOH [hours] stands for weighted overheating hours. A further developed review methods for thermal inside climate was published by the Dutch Government Buildings Agency in 1991. In this method, changes in clothing behaviour and air movement (extra ventilation during summer) are taken into account to determine the severity of overshooting the comfortable temperature. This method is the generally applied method in The Netherlands, also outside the Government Buildings Agency. The guideline value of the number of weighted overheating hours (called WOH) which represents a comfortable inside climate was set at 150 after extensive research.
§ ATG stands for Adaptive (temperature) Threshold Graph. This class is intended to replace the WOH method; the PMV-method remains useful in situations with exceptionally high metabolism or clothing resistance. Basically, the ATG is suitable for buildings with both high and low user influence, with open windows, or with fully closed facades.
•For regular offices Class B is often used as a starting point, e.g. during the design evaluation of a regular office;
•Class A ('Very good') suits buildings with a group of relatively sensitive users or buildings with extra high requirements on comfort (for example, a main office at a prime location);
•Class C is suitable in existing buildings or temporary buildings, e.g. during measurements in an old building after complaints were filed.
§ PMV [Index] stands for
Predicted Mean Vote, i.e. this represents the predicted average rating of the
buildings comfort by the occupiers. The PMV is a thermal index, derived from a
heat balance model for thermal comfort which was developed by Fanger. This index
predicts the thermal sensation of a large group of people in a thermal
environment which is specified by an average air- and radiation temperature,
average air speed, humidity, thermal insulation of clothing, and metabolism.
The indoor thermal climate is considered to be good if the PMV value does
not exceed +0.5 (given the combination of environment parameters, corrected for
instantaneous clothing insulation and metabolism). By Fanger’s definition, 90%
of the users should experience the climate as comfortable (only 10% votes +2 or
+3).
|
ISSO Publication 74 (2004) Thermal comfort - requirements for the indoor temperature in buildings
| |
|
|
NEN-EN-ISO 7730 Environment - Analytical determination and interpretation of thermal comfort by calculation of the PMV and PPD values and local thermal comfort
|
[Selection] BS
The counting hours indicate the period when the
selected requirements apply. Usually, this coincides with the use of the room
which means that the inside climate only needs to be controlled within the usage
period. A selection can be made from Schedule of counting hours.