
EPG BS
In this box it can be
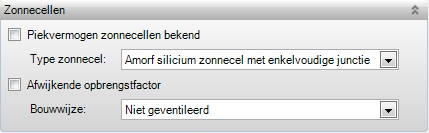
indicated whether the peak power of the PV-panels is known. After clicking the
checkbox an additional input field appears in which the peak power can be
specified. Note that if the peak power is specified a quality statement should
be presented.
EPG BS
If the total peak power
of the PV-panels is known it can be specified here in W/m2 as
indicated in the quality statement.
EPG BS
The type of PV-panel can
be indicated here in case the peak power of the PV-panels is unknown. The peak
powers which are used in the calculations for the various types of PV-panels are
presented in Table 20.2 of BS 7120.
•Mono crystalline silicon PV-panels are made of silicon slices cut from a big block of mono crystalline, in which the silicon atoms have been arranged in an orderly manner. The efficiency of mono crystalline silicon PV-panels ranges from 13 to 16% in practical applications.
•Multi crystalline silicon is cast and therefore simpler and cheaper to produce compared to mono crystalline silicon. The various crystal regions develop during the solidification process which results in its characteristic appearance. The efficiency of multi crystalline cells ranges 13 and 15% in practical applications, which is slightly lower than mono crystalline cells (Source: website PV Shop 2010)
•Amorphous silicon with single junction PV-panels are manufactured using a vapour deposition technique, which yields a relatively cheap mass production process. However, the efficiency is not as high (yet) as it ranges from 6 to 8%.
•Amorphous silicon with multi-junction PV-panels are stacks of multiple PV-panels, which all are sensitive to a different region of the solar spectrum. In this way a larger portion of the incident sunlight is converted into electric energy per unit of surface area of the PV-panel.
•Copper-Indium/Gallium-diselenide PV-panels are composed of copper, indium, gallium and selenium. A thin layer of molybdenum is applied on the substrate (a glass or a polymer). The efficiency of these PV-panels is 20%, they are relatively expensive however.
•Cadmium Telluride is, in addition to copper-indium/gallium-diselenide, applied in the new generation of thin-layer PV-panels. The material structures are similar, but different materials are applied as electrode. These PV-panels typically have an efficiency of approximately 15%.
|
EPG |
NEN 7120, paragraaf 20.3.2 Bijdrage van zonnestroomsystemen
|
EPG BS
Depending on the
integration of the PV-panels into the building a yield factor is determined. In
order to deviate from this value a different yield factor may be specified here.
In this case, a quality statement should be presented.
EPG BS
The yield factor of the
PV-panels can be specified here as shown in the quality statement.
EPG BS
The type of installation
of the solar panels can be specified if the yield factor is unknown. The yield
factors used in the calculations for the different installation methods are
given in Table 20.1 BS 7120.
•Unventilated (directly installed on roof or façade, i.e. without cavity)
•Moderately ventilated (installed on / inside the roof or façade)
•Highly ventilated (installed detached on an open supporting structure)
|
EPG |
NEN 7120, paragraaf 20.3.2 Bijdrage van zonnestroomsystemen
|