
The indoor environment in offices strongly influences the health and productivity of the people who work there. Improving the environment quality can lead to better health and increased productivity. The cost that poor environmental quality can entail is generally not included in economic calculations for building design and management. Often these calculations are limited to the total construction costs, energy and maintenance.
As a result, the climate control system not only directly affects the building operation costs, but also indirectly affects productivity and ultimately, revenue.
|
|
ISSO / REHVA 901 (2007) Indoor environment and productivity in offices Chapter 7 Calculation Procedure |
|
|
NOTE: This calculation method is representative of offices. The results of the productivity estimations in buildings with a different use are approximations. |
Specifies whether to display the results for a single
room, or multiple rooms
•Single room, shows the local effects on productivity
•Multiple rooms, shows the effects across multiple rooms, or the whole building. When this option is selected, extra inputs are required.
Defines from which room you want to view the Productivity
loss graph
|
|
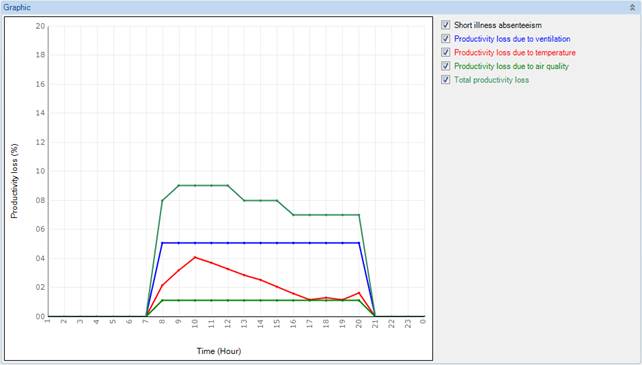
You can view only one room at a time in the graph. NOTE: Only the calculated areas are displayed. If the desired room is not present in the list, then it has not been calculated. |
[Date]
Specifies the
date when the graph is to start.
[Number]
The number of
people present on that day in the room
|
|
Enter the same number of people as specified in the calculation. |
[Rate] Default
100%
Percentage of total occupation in the room on that day
[Percentage] standard
5%
Percentage of total usage time over a full year in which the users are
absent because of illness.
This option specifies whether the majority of offices in
the building are open plan areas. An open plan office is an office with many
employees (usually more than 12) who are working together in the same room
without partitions. If the office is mostly open plan then there is a greater
risk of germs being transferred, thereby leading to more absence due to
sickness.
Specifies whether air recirculation occurs in the
building. If the air in a building is recycled germs may be more easily
transferred to other workers, leading to increased levels of sickness.
|
|
This option should also be selected if the AHU has a mixing box, or a heat recovery system. |
[Percentage] standard
10%
The limit of the percentage of people dissatisfied with air quality.
The quantitative relationship shows a performance increase of 1.1% for every 10%
reduction in the number of people dissatisfied with the air quality, among a
number of 25-70% dissatisfied. This corresponds to a performance increase of
0.50% for each decipol reduction within the band 2-13 decipol. Decipol is a
quantitative measurement of perceived air quality based on sensory perceptions
by subjects (Fanger 1988).
The type of work being undertaken will affect the air
quality. The more active the user is, the greater the effect poor air quality
will have on productivity.
•General office has a higher activity and needs to be more strongly ventilated
•Only typing work requires less activity and does not need to be as strongly ventilated