
BS EPG
The name of a generator
is generated automatically based on its the type and subtype. After the
selecting the correct type and subtype, this name can be modified as
desired.
BS EPG

The
system specifies what the generator is used for.
§ Heat generator for heating
§ Cold generator for cooling
§ Domestic hot water generator for domestic hot water
§ Combi heat generator for heating and domestic hot water
EPG
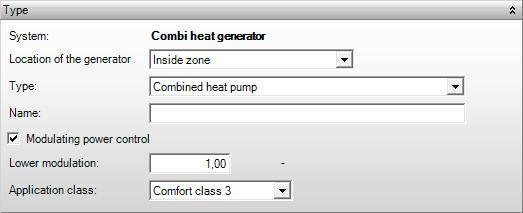
The location of the
generator can be indicated here. This location is only taken into account for
individual boilers for which the efficiency is determined flat rate. The
location does not make a difference for all other generators. The option 'Inside
zone’ indicates the generator is ‘located within the boundaries of the EPG
calculation’. For the other options the calculations are performed with the
generator 'placed outside the boundary of the EPG calculation'.
§ Inside zone generator is placed INSIDE the boundary of the EPC calculation.
§ Inside building and outside zone generator is placed OUTSIDE the boundary of the EPC calculation
§ Against building generator is placed OUTSIDE the boundary of the EPC calculation
§ Inside parcel generator is placed OUTSIDE the boundary of the EPC calculation
§ Outside parcel generator is placed OUTSIDE the boundary of the EPC calculation
•
|
|
NEN 7120, Table 14.11 |
EPG
This
box indicates whether the generator within the system is default. This option is
only relevant if multiple generators have been defined for heat, cold, or
domestic hot water; in case only one generator has been defined it will
automatically be the default one. If multiple generators have been defined for
heat, cold, or domestic hot water, but no default generator has been specified,
then a default generator is chosen in accordance with the rules in the NEN 7120.
If the rules are violated in specifying the default generator, a message is
displayed by the EPG calculation.
|
|
NEN 7120 |
EPG
The type of the
generator can be selected from a presented list of options. This list is
generated depending on the configuration of the generation (individual or
collective) and the selected system (heat, cold, domestic hot water, or combi).
An overview of the generator for different configurations and systems is
presented below:
Heat generator (individual and collective systems)
§ Boiler for heating.
§ Heat pump for heating; this is a device which raises sustainable heat from the near environment from a low to a high and useful temperature level. This heat can be extracted from the environment: the soil, water, air, waste heat, etc. Driving the heat pump only requires a limited amount of primary energy. By utilizing sustainable energy, the heat pump can save up to about 50% primary energy compared to a boiler. The energy source only heats up the central heating. (Source and more information: SenterNovem)
§ Cogeneration (CHP / micro-CHP), or CHP boiler, for heating; this is a boiler which produces electricity in addition to heat in case heating is required in the building. The energy is produced from the same energy source. The energy source may be natural gas, biogas, propane, butane, or hydrogen. Besides the economic benefit to the consumer due to lower energy costs, (micro) CHP also benefits the environment as the energy consumption and CO2 emission are reduced. The energy source only heats up the central heating. (Source and more information: SenterNovem)
§ Solar heating system for heating.
§ External heat
source for heating, which is also referred to as ‘heat distribution’ or
‘district heating’; this uses waste heat from power plants (CCGT / gas), waste
incineration plants, industries and biomass plants. This heat is then
transferred to the target location using a distribution network such as water.
The energy source only heats up the central heating. (Source and more
information: SenterNovem)
Cold generator (individual and collective systems)
§ Compression chiller, or heat pump, for cooling; this is a chiller in which a compressor draws in a cooling agent at a low pressure. Due to compression, the pressure of the cooling agent is elevated resulting in a rising temperature. The compressor is driven electrically. The hot cooling gas is subsequently transferred to the condenser and condensed into a liquid state. Then the pressure is reduced in the expansion valve after which the liquid cooling agent evaporates in the evaporator at this low pressure. During this process heat is extracted from the water (indirect expansion cooling), or from the air (direct expansion cooling). So heat is extracted (=cooling) from the environment (water or air). This heat is deposited into e.g. the outside air in the condenser. (Source: SenterNovem)
§ Absorption chiller for cooling purposes; this is a chiller which is driven with waste heat from a sufficiently high temperature level (> 110 ° C). This may be e.g. heat released by the production of electricity (building-related CHP) or district heating (external heat delivery). The use of primary energy in an absorption chiller is about twice as high compared to a compression chiller at the same cooling capacity. However, the noise production is significantly lower, meaning the absorption chiller may be a viable option in case severe requirements on the noise level apply. (Source: SenterNovem)
§ Cold storage or soil cooling without the use of a chiller. The heat pump is used for passive cooling rather than active cooling.
§ Dew point cooling
§ External cold source for cooling
|
BS |
ISSO 43
|
Domestic hot water generator (individual systems)
§ Gas water heater which is an individual boiler for domestic hot water
§ Kitchen geyser which is an individual geyser for domestic hot water. This is a device which can deliver hot water, enough to heat up a large amount of water to do e.g. the dishes.
§ Electric water heater which is an individual electric water heater for domestic hot water
§ Heat pump water heater which is an individual heat pump water heater for domestic hot water using ventilation exhaust air as its supply source. A heat pump water heater contains a thermal barrel in which a supply of hot water is kept. The heating of this water content is performed using a heat pump.
§ Cogeneration (CHP / micro-CHP) for domestic hot water
§ Solar water heater for domestic hot water
Combi heat generator (individual systems)
§ Combi boiler (gas) for heating and domestic hot water
§ Combi heat pump for heating and domestic hot water
§ Cogeneration (CHP / micro-CHP) for heating and domestic hot water
§ Solar combi-system solar water heater for heating and domestic hot water
§ External heat source for heating and domestic hot water
Domestic hot water generator (collective systems)
§ Gas water heater contains a tank in which a supply of hot water is kept. Heating of the supply water is performed using gas. Gas water heaters and electric water heaters are used directly heated storage barrels for hot domestic water in collective systems. A combination with other generators is not possible in this case. A sub-screen ‘Storage tanks’ appears in which the volume of the storage barrels can be specified. The volume is applied to determine the default generator in case multiple gas water heaters and / or electric water heaters have been defined.
§ Electric water heater contains a storage tank in which a supply of hot water is kept. Heating of the supply water is performed using electricity. Gas water heaters and electric water heaters are used directly heated tanks for hot domestic water in collective systems. A combination with other generations is not possible in this case. A sub-screen ‘Storage tanks’ appears, see Gas water heater.
§ Heat exchanger indirectly heated storage tanks is a collective system for domestic hot water with indirectly heated storage tanks which may be combined with a boiler, heat pump, CHP, or external heat delivery. A sub-screen ‘Storage tanks’ appears in which the insulation thickness of the storage barrels can be specified (flat rate method only; detailed method in not yet available).
§ Heat delivery system (residential) Heat for domestic hot water can be distributed from the system of block heating using a delivery system for domestic hot water in case a heating system with block heating is applied. Both the generators for the collective heating system and the delivery system for domestic hot water need to be specified.
§ Boiler for hot water. This generator can be used only in combination with the heat exchanger in a system with indirectly heated storage barrels.
§ Heat pump for domestic hot water. This generator can be used only in combination with the heat exchanger in a system with indirectly heated storage barrels.
§ Cogeneration (CHP) for domestic hot water. This generator can be used only in combination with the heat exchanger in a system with indirectly heated storage barrels.
§ Solar heating system for domestic hot water
§ External heat
source for domestic hot water. This generator can also be applied in
combination with a heat exchanger in a system with indirectly heated storage
tanks.
Combi heat generator (collective systems)
§ Boiler for heating and domestic hot water. This generator can be used only in combination with the heat exchanger (domestic hot water) in a system with indirectly heated storage barrels for domestic hot water.
§ Heat pump for heating and domestic hot water. This generator can be used only in combination with the heat exchanger (domestic hot water) in a system with indirectly heated storage barrels for domestic hot water.
§ Cogeneration (CHP) for heating and domestic hot water. This generator can be used only in combination with the heat exchanger (domestic hot water) in a system with indirectly heated storage barrels for domestic hot water.
§ Solar heating system for heating and domestic hot water. This option cannot be included in the EPG calculation.
§ External heat source for heating and domestic hot water. This generator can be used only in combination with the heat exchanger (domestic hot water) in a system with indirectly heated storage barrels for domestic hot water.
EPG
In case the generator
type is a boiler for heating, it can be specified whether this boiler contains a
pilot. If so, additional thermal auxiliary energy use is charged.
|
|
NEN 7120, paragraph 14.6.5 |
EPG
In case the generator
type is a boiler for heating and / or domestic hot water, its heat certificate
can be specified. This certificate affects the calculations of the flat rate
efficiency.
§ Conventional efficiency boiler with an efficiency of 70-80%. The source only heats the central heating.
§ Improved efficiency boiler is a boiler stoked with gas which has a full load efficiency of at least 88.7% on lower value. The source heats only the central heating.
§ High efficiency 100 boiler is a boiler stoked with gas which has a partial load efficiency of at least 100% on lower value. In The Netherlands it may also be a boiler which obtained the required quality mark from the Keuringseisen van Gastoestellen (Gaskeur CV-HR). The source heats only the central heating.
§ High efficiency 104 boiler is a boiler stoked with gas which has a partial load efficiency of at least 104% on lower value. In The Netherlands it may also be a boiler which obtained the required quality mark from the Keuringseisen van Gastoestellen (Gaskeur CV-HR). The source heats only the central heating.
§ High efficiency 107 boiler is a boiler stoked with gas which has a partial load efficiency of at least 107% on lower value. In The Netherlands it may also be a boiler which obtained the required quality mark from the Keuringseisen van Gastoestellen (Gaskeur CV-HR). The source heats only the central heating. (Source:SenterNovem)
|
|
NEN 7120, tables 14:11 and 19:19 | |
|
|
NEN-EN 677
| |
|
BS |
ISSO EPA W | |
EPG
A power control can
be specified here in the case of a generator for heating. The power control
effects charging the auxiliary energy use of the generator.
EPG
If modulating power
control has been applied, then the lower level of modulation can be specified in
the range from 0.4 - 1.0. In case the specified limit is below 0.4, then the
standard of 0.4 is assumed.
EPG
In case of a boiler
for heating, it should be specified whether this boiler is fired by gas or oil.
This choice can be made only if the heat certificate is ‘Conventional
efficiency’.
§ Gas gas-fired boiler
§ Oil oil-fired boiler
In case of a compression chiller (cold generator) it should be specified whether it concerns a compression chiller driven by a gas engine or by electricity.
§ Gas engine gas engine driven compression chiller (or heat pump)
§ Electricity electrically driven compression chiller (or heat pump)
EPG
The specifications of
a compression chiller (cold generator) are specified from this selection list.
The flat rate efficiency is determined based on these specifications.
Additionally, the auxiliary energy use to dispose the cooling power of the cold
generation is determined using these specifications. The specification ‘high
temperature delivery system’ is not included in the selection list as this is
passed on to the cooling system in the resource ‘Distribution’.
§ Not specified
§ Dry cooler
§ Evaporation condenser
§ Wet cooling tower
§ Low temperature cold source
|
|
NEN 7120, tables 17.6 and 17.8 |
EPG
In case of a
compression chiller or absorption chiller, this box indicates whether the wet
cooling tower or evaporation condenser is a closed circuit. This property is
taken into account to determine the auxiliary energy required to dispose the
cooling power.
EPG
This box indicates
that the pumps of the cooling water circuit between the cooling machine and
cooling source, or the ventilators of the air-cooled condensers or cooling
towers, have speed control. This property affects the determination of auxiliary
energy required for the generation of the cooling system.
EPG
For the gas-driven
compression chiller you may deviate from the flat rate thermal conversion factor
by manually specifying its value.
|
|
NEN 7120, tables 17.6 and 14.17 |
EPG
The shaft power of the
engine of the gas-driven compression chiller should be specified in order to
determine the thermal power of the cold generator.
EPG
Checking this box
indicates the compression chiller is an air-water heat pump. This option is not
included in the EPG calculation; however, it is passed to the EPCheck program.
This program is used to easily assess whether the EPG calculation contains major
errors.
EPG
In case cold storage is
applied as cold generator, the flow of groundwater or the flow through the soil
heat exchangers should be specified to determine the thermal cooling power.
EPG
The certificate for
domestic hot water should be specified for the (combi) boiler or hot water
system in order to determine the flat rate efficiency of the (combi) boiler.
§ No: no certificate applicable;
§ CW: certificate comfort water is applicable;
§ HRww: certificate high efficiency hot water is applicable.
|
|
NEN 7120, tables 19.16 |
EPG
The
Gaskeur-CW-comfort class (Dutch) certificate should be specified for a (combi)
boiler or hot water system. This certificate is applied to determine the flat
rate efficiency of the (combi) boiler.
§ Comfort class 1 'sink' for kitchen use only.
§ Comfort class 1* is equivalent to Comfort class 1 with the addition night shower tapping of Comfort class 2 of 3.5 dm3/min
§ Comfort class 2 certificate high efficiency is applicable
§ Comfort class 3 domestic hot water flow of at least 6 dm3/min at 60º, and filling a bath tub with 100 dm3 water at 40º within 12 min.
§ Comfort class 4 domestic hot water flow of at least 7.5 dm3/min at 60º, and filling a bath tub with 120 dm3 water at 40º within 11 min.
§ Comfort class 5 domestic hot water flow of at least 7.5 dm3/min at 60º, and filling a bath tub with 150 dm3 water at 40º within 10 min.
§ Comfort class 6 domestic hot water flow of at least 7.5 dm3/min at 60º, and filling a bath tub with 200 dm3 water at 40º within 10 min.
•
|
|
NEN 7120, tables 19.16 |
•