
BS EPG
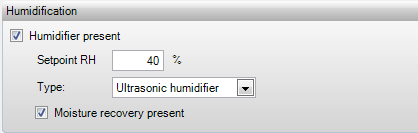
This box allows
you to indicate whether a humidifier/dehumidifier is present and should be taken
into account in the calculations. The specifications of the dehumidifier can be
indicated in this screen. The effectiveness of the coil is determined based on
the thermal power delivered at a given water supply temperature, air supply
temperature, and moisture conditions. The software is able to determine the
maximum thermal power under various conditions (air volumes, supply
temperatures, moisture content, etc). The true air volumes (in the given
conditions) are specified from the supply fan, and the supply temperatures from
the heating curves for water and air. The cooler/ dehumidifier is controlled
based on temperature and moisture content.
[%
RH] BS
The setpoint determines when the system must
humidify/dehumidify the air. This part is activated when the relative humidity
is below the setpoint for humidification and above the setpoint for
dehumidification. The moisture conditions are important as these determine the
effectiveness of the cooling coil for a large part in case of
dehumidification.
|
BS |
ISSO Publication 32 (2011), Section 5.3 Design Criteria for humidity
|
EPG
The type of
humidifier is only applicable for EPG calculations (Source: SenterNovem).
If the selected type is the electricity-driven steam vaporizer, then the energy
source will be electricity in the EPG calculation. For the other types, the
required energy is provided by the heating system and whatever generator is
specified for.
•Gas-driven steam vaporizer. Steam is blown into the air through a tube with holes. The steam is generated in one or more small gas boilers by the evaporation of water. These devices heat up water using a heating element driven by gas. The obtained vapour is added to the air in a controlled way.
•Electricity-driven steam vaporizer. Steam is blown into the air through a tube with holes. The steam is generated in one or more small electric boilers by the evaporation of water. These devices heat up water using a heating element driven by electricity. The obtained vapour is added to the air in a controlled way.
•Ultrasonic humidifier. In this method, water is atomized by means of ultrasonic vibrations in aerosols. The air in the channel in which these vibrations take place absorbs these aerosols quickly. The movement of air is achieved using a ventilator. The relative humidity can be kept at a high level with this method.
•Adiabatic humidifier. The humidifier works through the expansion and contraction of air; literally adiabatic means: without heat exchange with the environment. So no heat exchange occurs in an adiabatic process, but rather compression leads to heating and expansion to cooling.
[%] BS
The setpoint determines when the system must
humidify/dehumidify the air. This part is activated when the relative humidity
is below the setpoint for humidification and above the setpoint for
dehumidification. The moisture conditions are important as these determine the
effectiveness of the cooling coil for a large part in case of
dehumidification.
EPG
In this box it can be
indicated if moisture recovery is present. If this is the case, a reduction to
the energy need for humidification is surcharged.
|
|
NEN 7120, Section 18.2 |