
The heating curves are important for optimization and energy reduction in distribution networks.
BS EPG
The division into HT- and LT- systems can be
specified here depending on the heat generation and distribution. The generation
efficiency and distribution efficiency in the EPG calculation are based on this
temperature level.
•LT (Low Temperature): low temperature system. For EPG calculations, please consult NEN 7120, Tables 14.12 and 17.2.
•HT (High Temperature): high temperature system.
|
|
Choosing the temperature level LT / HT has an effect on the selection of the emissive devices. This means you can only link an LT distribution network to an LT emissive device and vice versa. | |
|
|
NEN 7120, Tables 14.12 and 17.2 | |
BS
This selection indicates the determination of the
heating curve. Three possibilities are available:
•Default: the heating curve is determined using a default value, irrespective of daytime operation or night time operation, and irrespective of the outside temperature. The default temperature is 80 °C for heating, 35 °C for LT heating, 6 °C for cooling, 17 °C for HT cooling, and 18 °C for heating and cooling together;
•User defined: the heating curve has constant values as specified for daytime operation and night time operation;
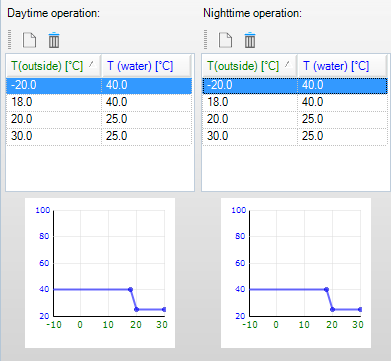
•Heating curve: the heating curve is specified manually. For all values of outside temperature (Toutside) a value of the heating- or cooling water (Twater) can be specified. Separate curves can be defined for daytime operation and night time operation.
|
BS |
ISSO Publication 32 (2011), Section 5.2 Temperatures of plants
|