
HL BS CL EPG
The frame is the
part of the complete surface area of the window that includes a frame, either
expressed as surface percentage (%) or frame thickness (mm).
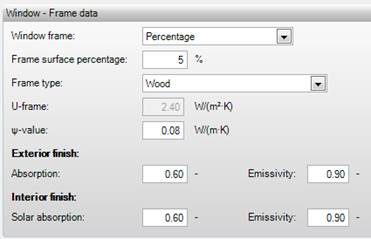
§ The frame surface percentage (5% by default), is the percentage of window frame surface with respect to the total window surface;
§ The frame thickness (67 mm by default), or width of the frame, is the gross width of the frame edge. Vabi Elements computes the surface area of the window frame based on this frame thickness by assuming a single frame around the window. This means saddle bars and mullions are not taken into consideration. If these saddle bars and mullions need to be part of the calculations, we advise to calculate the frame surface percentage manually.
|
Houses | ||
|
Window surface [m²] |
Frame surface percentage [%] | |
|
Metal frame |
Wooden or plastic frame | |
|
0.5 |
30 |
35 |
|
0.75 |
25 |
30 |
|
1.0 |
20 |
15 |
|
1.5 |
16 |
11 |
|
2.0 |
14 |
10 |
|
2.5 |
12.5 |
8 |
|
3 and bigger |
11.5 |
7 |
|
With opening windows |
30 | |
|
Without opening windows |
15 | |
|
|
ISSO Kleinte Koellast (2010) tabel 3.6 Glaspercentage, afhankelijk van het totale raamoppervlak
|
|
|
ISSO Publicatie 32 (2011) paragraaf 1.2 Glasoppervlakte en raamoppervlakte
|
HL BS
CL EPG
In this field the U-value of the window frame is determined
based on a chosen standard frame type in accordance with ISSO 8, Table 7. A user
defined U-value may be specified if the value is known.
|
Frame Type |
Frame U-value (W / m². K) |
|
Wood |
2.4 |
|
Plastic |
2.0 |
|
Metal |
5.9 |
|
Thermally broken metal |
2.7 |
Table4: Predefined frame types (ISSO 8)
HL BS CL EPG
This is the
thermal transmission of the window frame. A well-insulated window frame is
characterized by a low U-value.
Standard 0.08 EPG
This value represents the linear thermal bridge
between the glass and the frame. This linear thermal bridge is calculated over
the circumference of the glass, which is the circumference of the window minus
the thickness of the frame. A well-insulated window frame is characterized by a
low PSI-value.
|
EPG |
NEN 1068:2012 Bijlage K Thermal insulation of buildings - calculation |
Standard 0.6 CL BS
The absorptivity is the heat or cold which can be
absorbed by the surface of a construction relative to the specific heat of the
material. This characteristic depends on e.g. the surface finishing such as
colour and coating, and the type of material. The absorptivity holds for short
wave solar radiation, whereas emissivity considers the long wave solar
radiation. Consequently, the absorptivity and emissivity do not have to be equal
to each other. Common values for the absorption coefficient can be found in Absorption
coefficients.
Standard 0.9 BS
The emissivity is the heat or cold which can be
emitted by the surface of a construction relative to the specific heat of the
material. This characteristic depends on the type of material; metal surfaces
generally have a lower emission coefficient. The emissivity considers long wave
solar radiation, whereas absorptivity holds for short wave solar radiation.
Consequently, the absorptivity and emissivity do not have to be equal to each
other. Common values for the emission coefficient can be found in the section on
Emissivity.